Ancillary services markets enable the trading of essential grid services like frequency regulation and voltage control, ensuring grid stability.
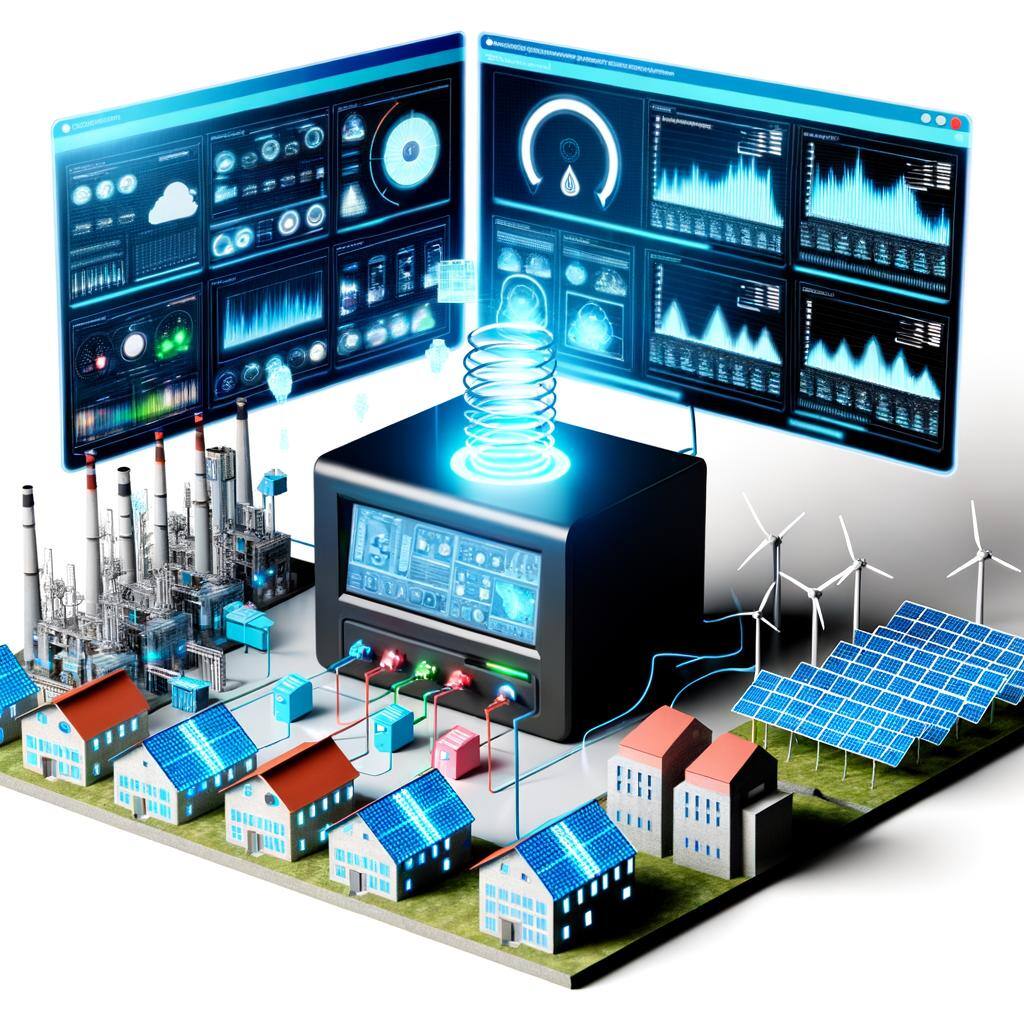
Wholesale market platforms facilitate large-scale energy trading between producers, consumers, speculators, and retailers, enhancing transparency, liquidity, and efficiency in the energy sector.
ETRMs are software systems that help energy companies manage trading operations, risks, and compliance with regulatory requirements, while also providing market analysis and automation tools.
Algorithmic trading automates energy commodity trades using computer algorithms, improving market efficiency, liquidity, and price stability, while also posing risks like systemic instability.
Price forecasting in the energy sector predicts future energy prices using historical data, market analysis, and statistical models informing decision-making, risk management, and strategic planning.
Renewables forecasting predicts energy output from sources like solar and wind using weather data and advanced modeling. It's essential for grid stability.
Load forecasting predicts future electricity demand using historical data, weather, and economic factors. It's essential for grid stability, resource optimization, and cost reduction.
Energy Management Systems optimize energy use, enhance efficiency, and support sustainability by monitoring and controlling energy resources in real-time across various sectors.
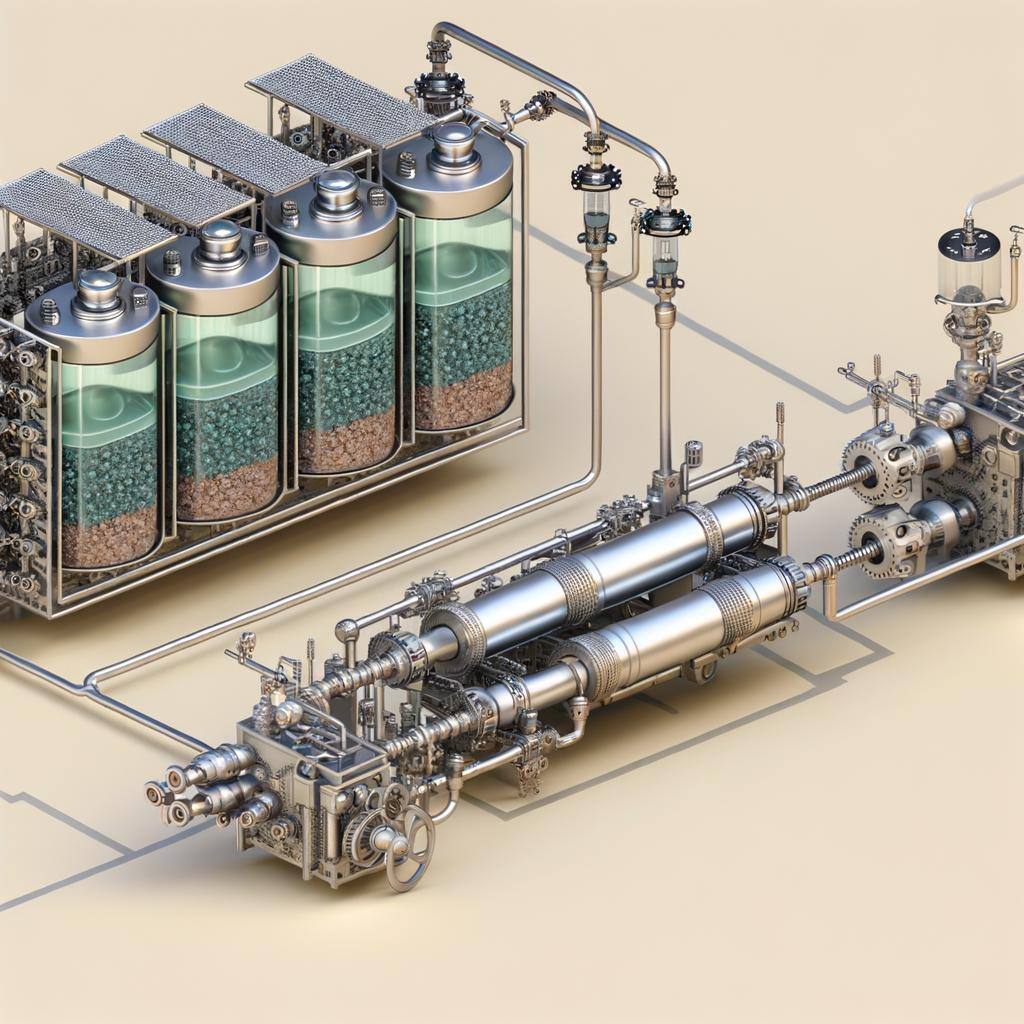
Hydrogen storage is vital for energy, transport, and industry, using methods like compressed gas, liquid hydrogen, and chemical storage to safely store hydrogen efficiently.
Flow batteries store energy in liquid electrolytes within external tanks, offering scalable, long-cycle energy storage for grid stability, renewable integration, and backup power systems.
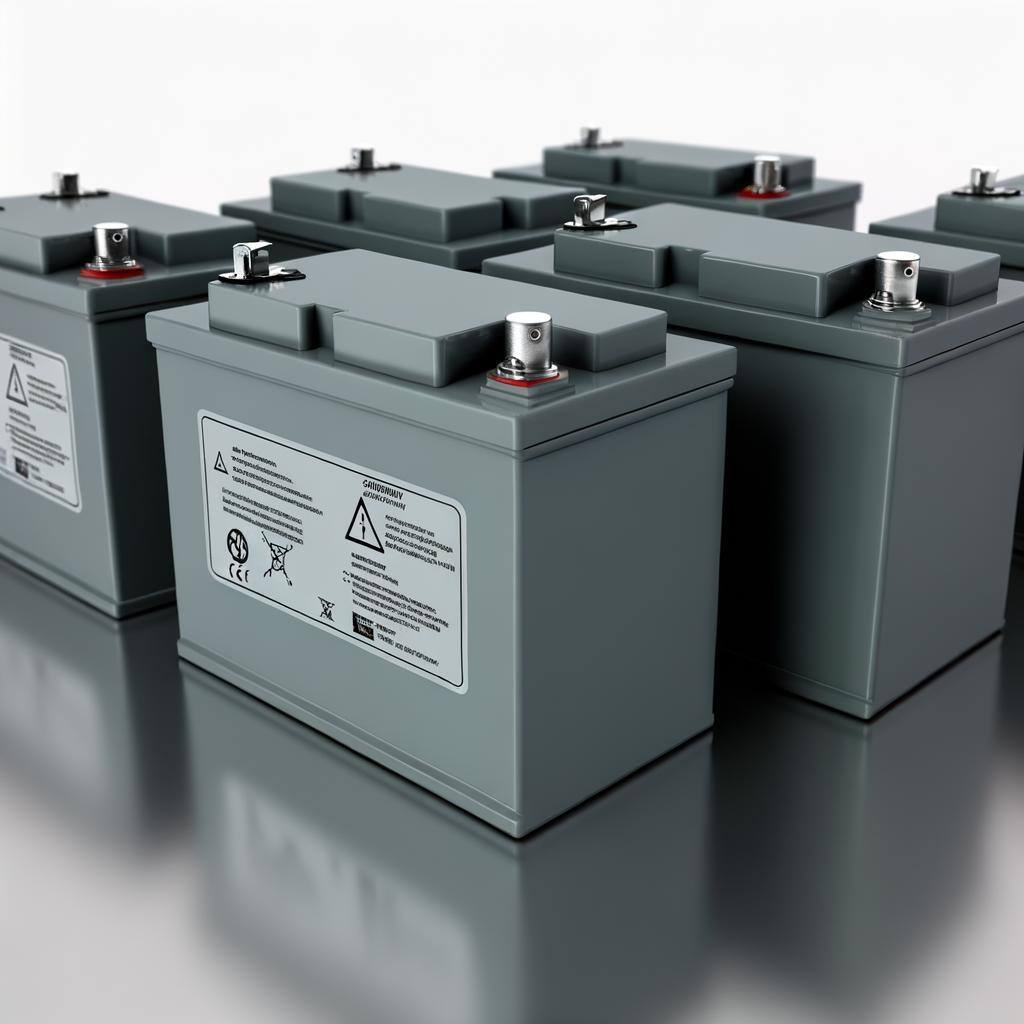
Lead-acid batteries store energy using lead dioxide, sponge lead, and sulfuric acid, offering reliable, low-cost energy storage for automotive, backup power, and off-grid use.
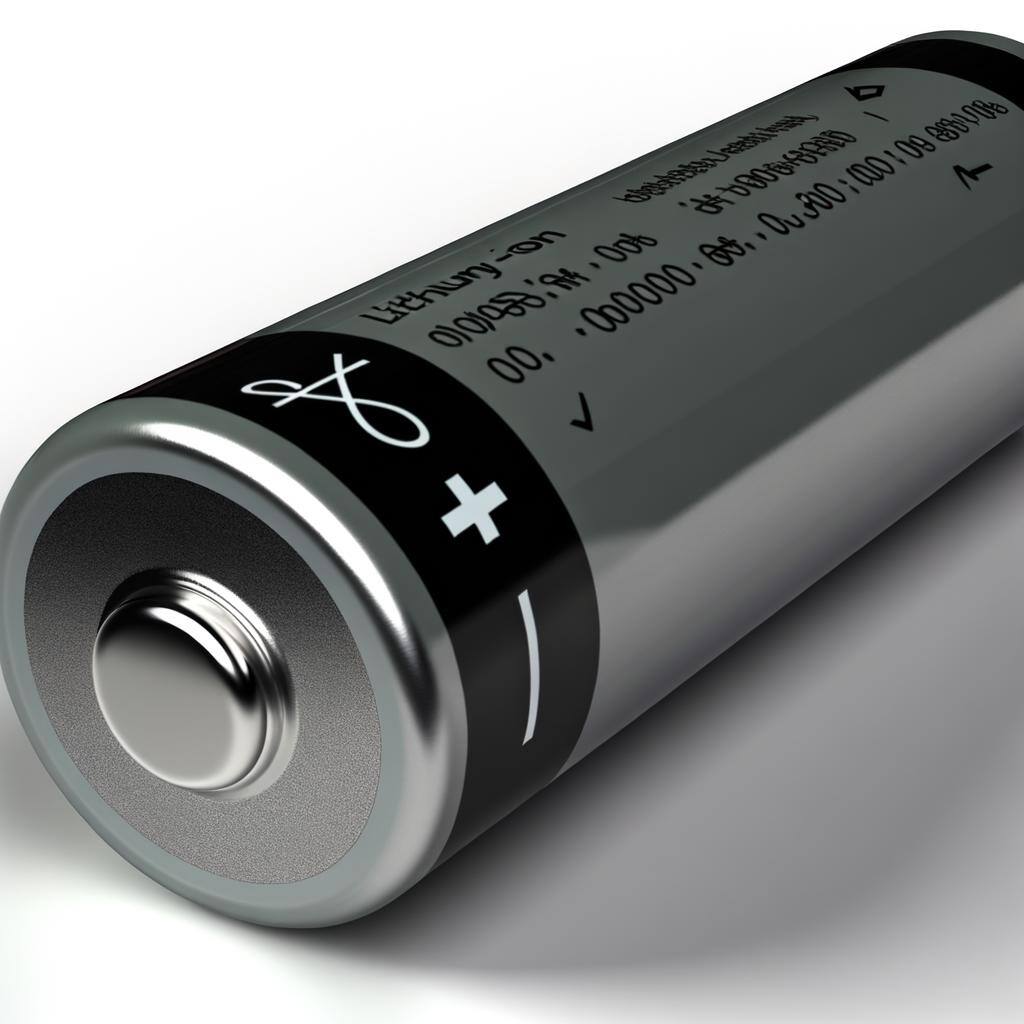
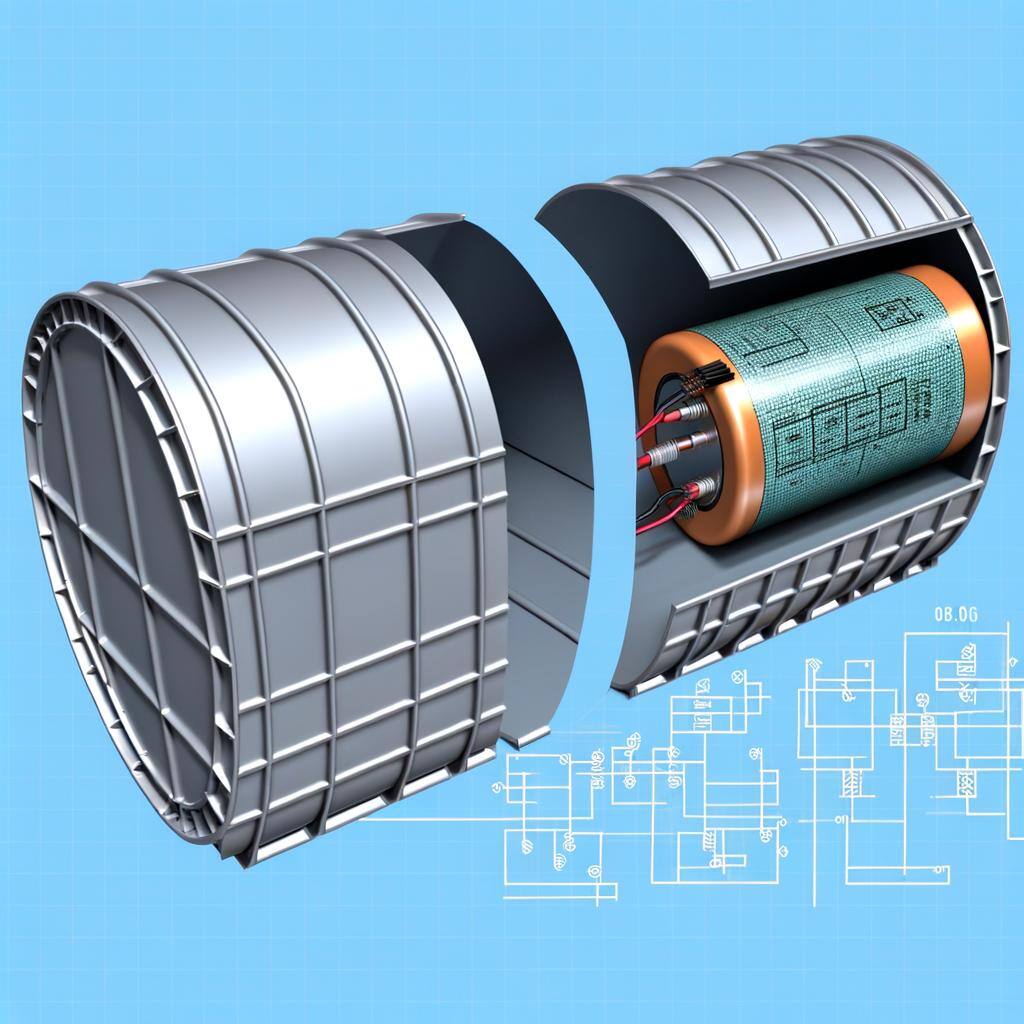
Lithium-ion batteries are high-energy, rechargeable batteries used in electronics, EVs, and renewable energy storage, offering efficiency, long life, and essential grid stability support.
Supercapacitors, or ultracapacitors, are energy storage devices that offer high power density, rapid charge/discharge, and long cycle life, ideal for quick energy delivery and renewable integration.
Capacitors store energy in an electric field between conductors, offering high power density, rapid charge/discharge, and crucial support for power conditioning and renewables.
Thermal energy storage (TES) stores heat or cold for later use, enhancing energy efficiency, supporting renewables, and reducing costs and emissions in HVAC, industrial, and power systems.
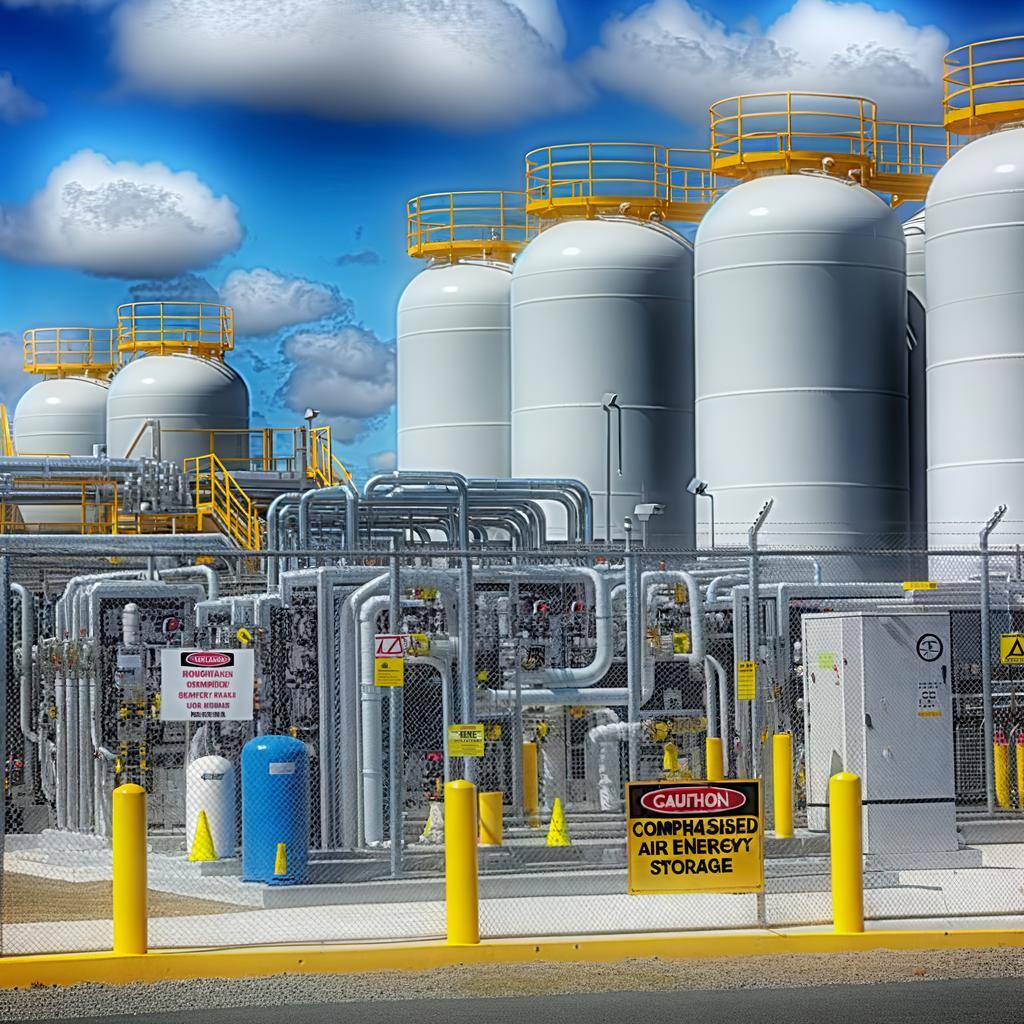
Compressed air energy storages store energy by compressing air and releasing it to generate electricity, balancing supply and demand, supporting grid stability, and integrating renewable sources.
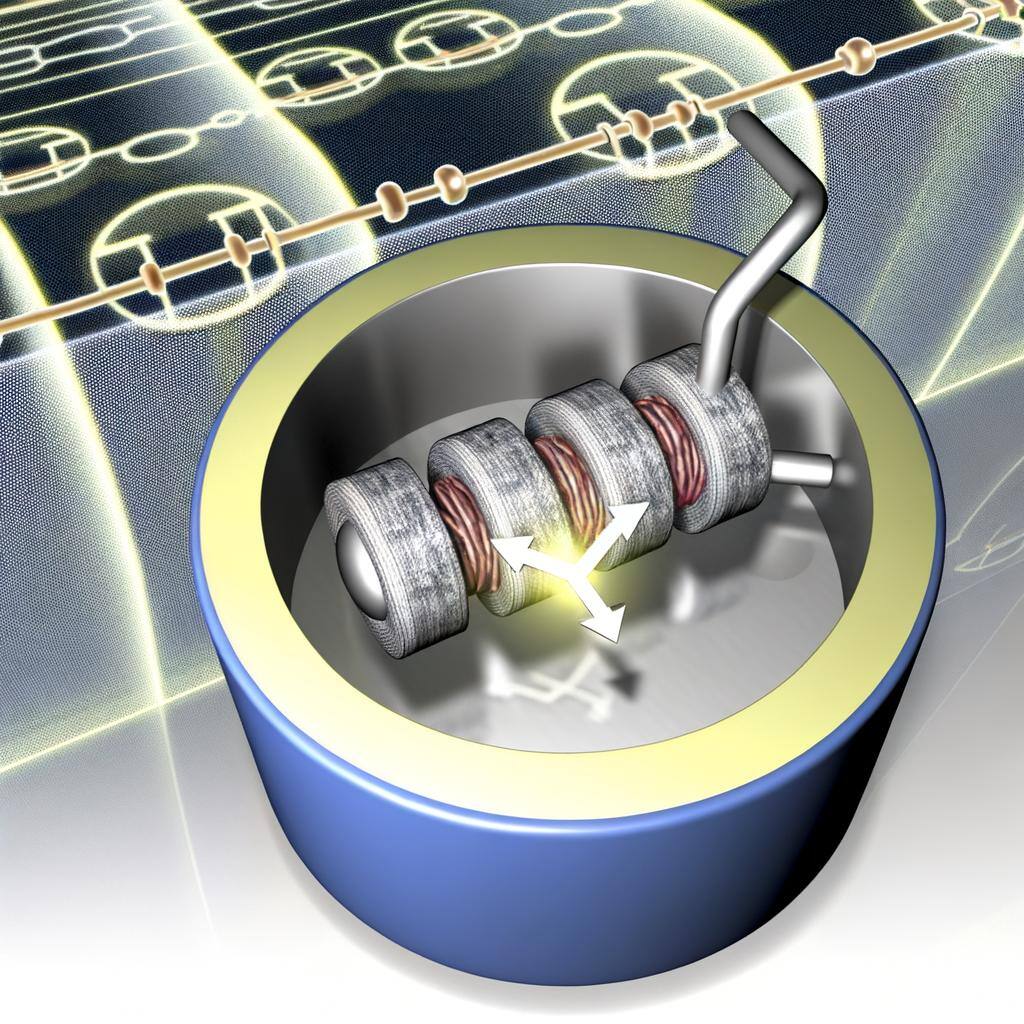
Flywheel energy storage stores kinetic energy by spinning a rotor at high speeds, offering rapid energy release, enhancing grid stability, supporting renewables, and reducing energy costs.
Pumped hydro storages store energy by pumping water to an upper reservoir and releasing it to generate electricity, balancing supply and demand, and supporting renewable energy integration.
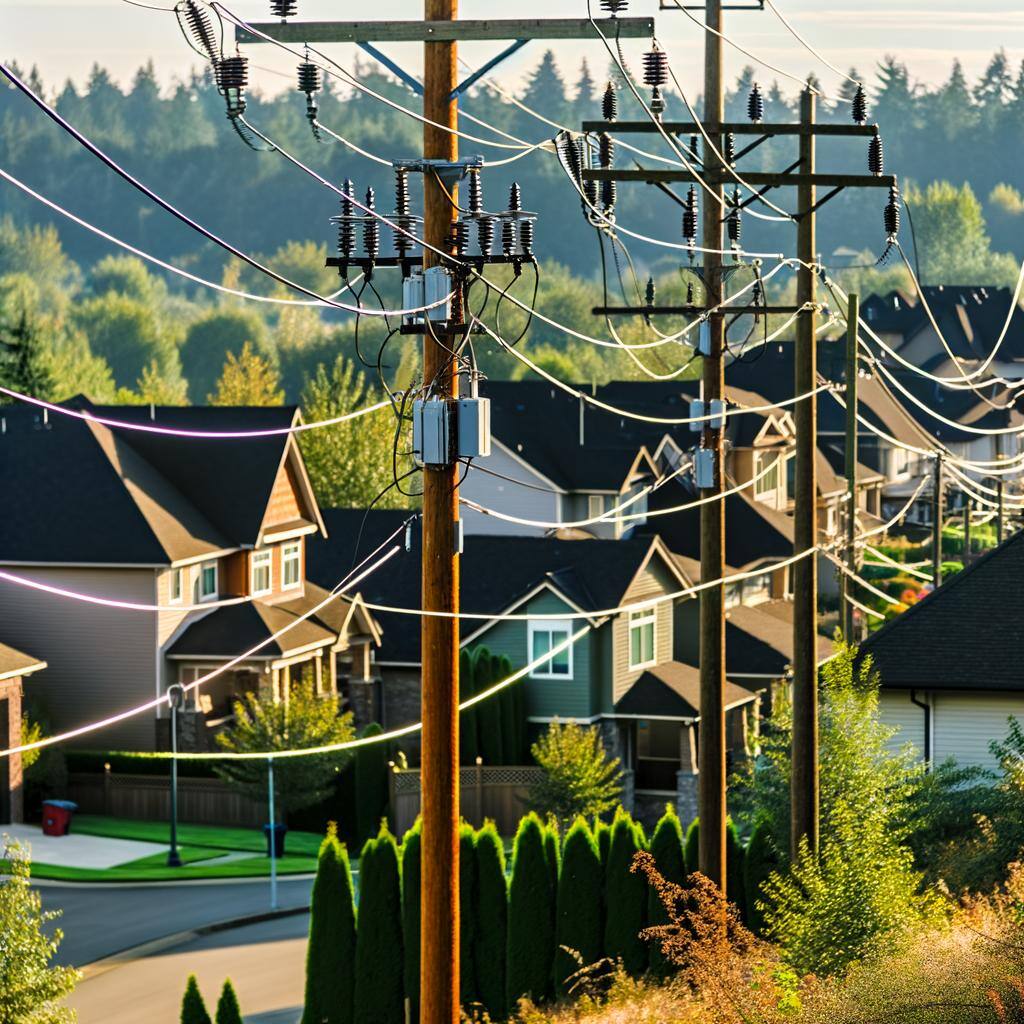
Distribution lines carry lower-voltage electricity from substations to consumers, ensuring safe and reliable power delivery, and play a role in integrating renewable energy into the grid.
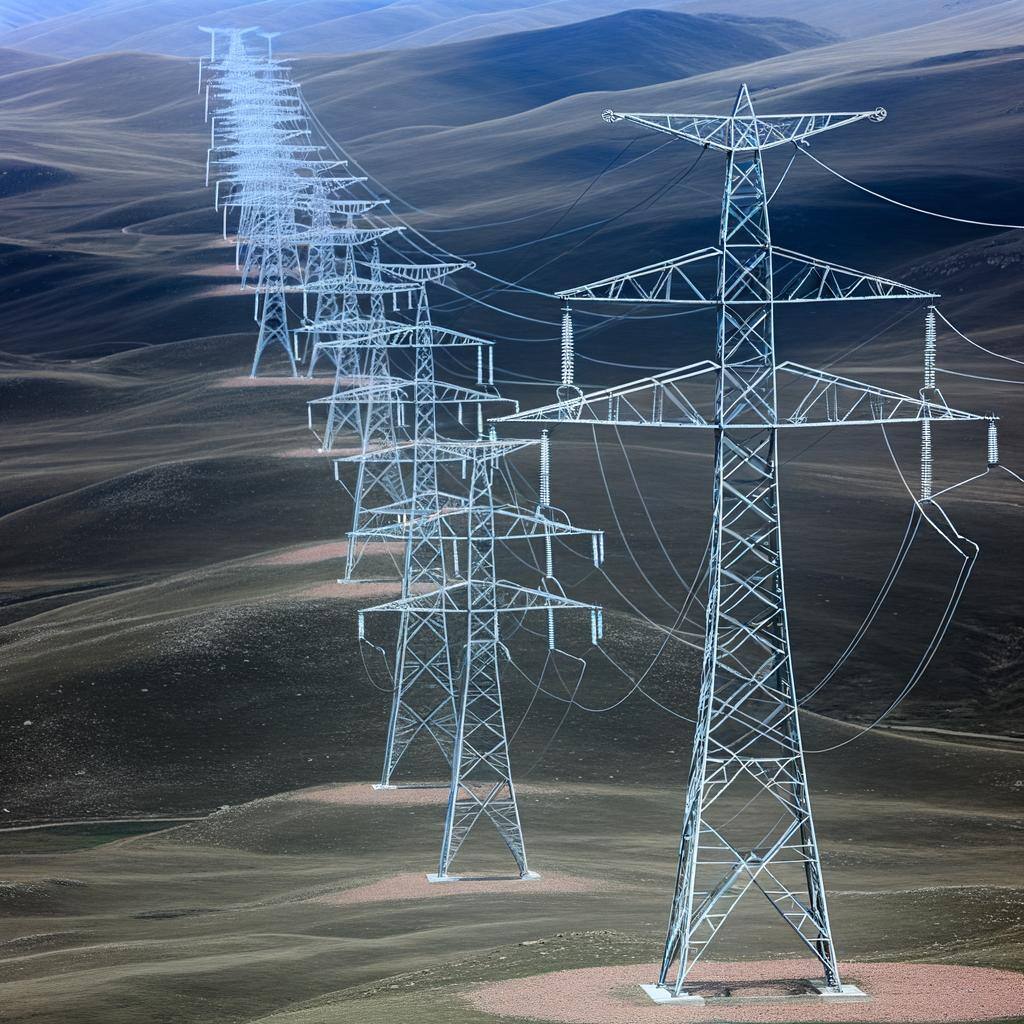
Transmission lines are high-voltage power lines that transport electricity from power plants to substations over long distances, ensuring efficient delivery.
A transformer changes voltage levels to enable efficient electricity transmission and distribution, crucial for grid stability and integrating renewable energy sources.
Electricity demand is driven by technology, policy, and consumer preferences, with key impacts from electrification, industrial needs, residential use, and commercial activities.
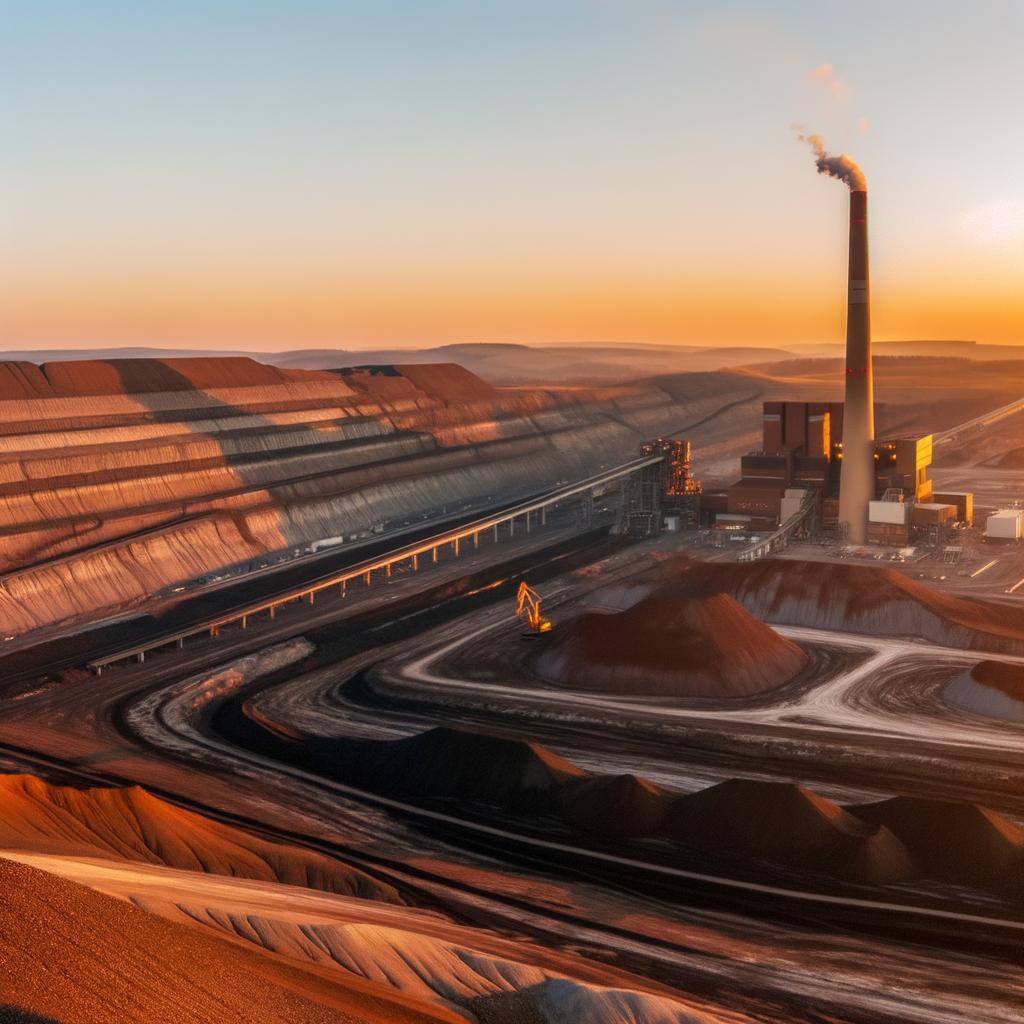
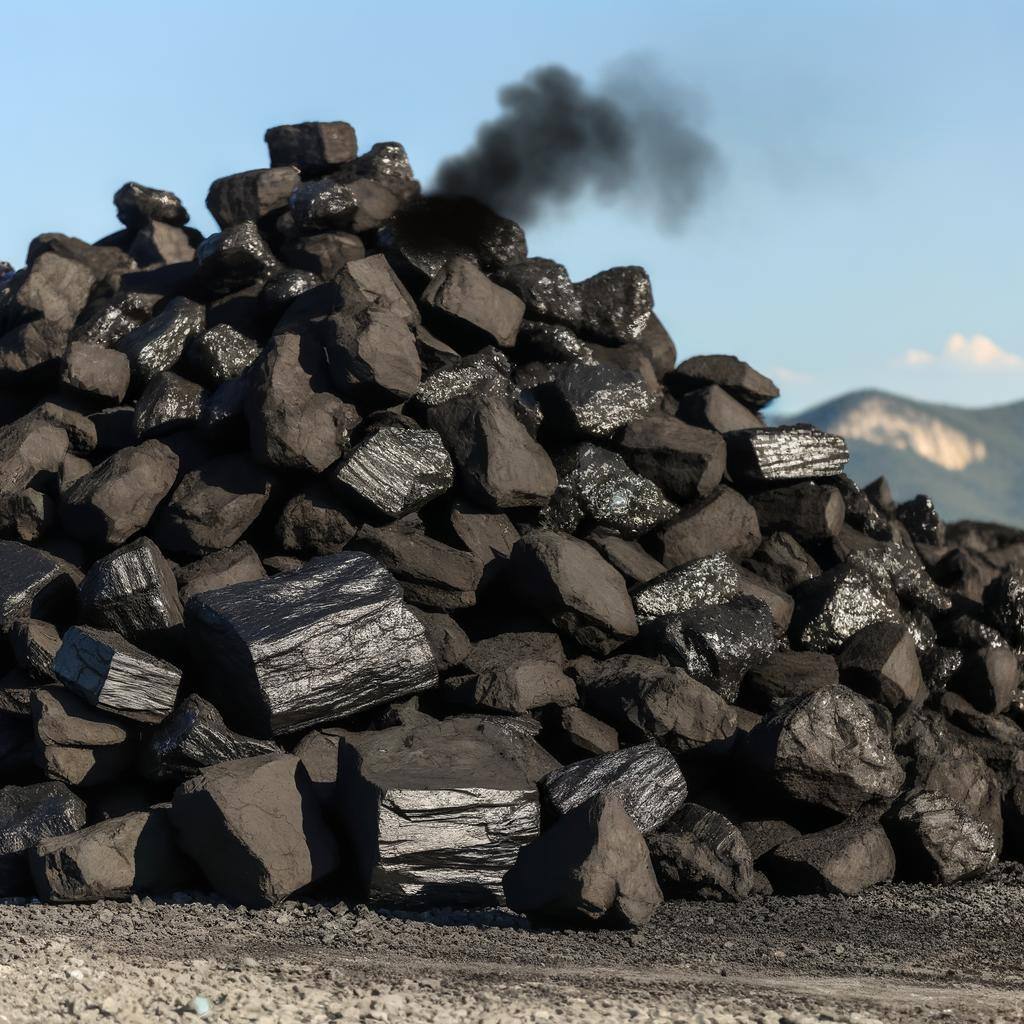
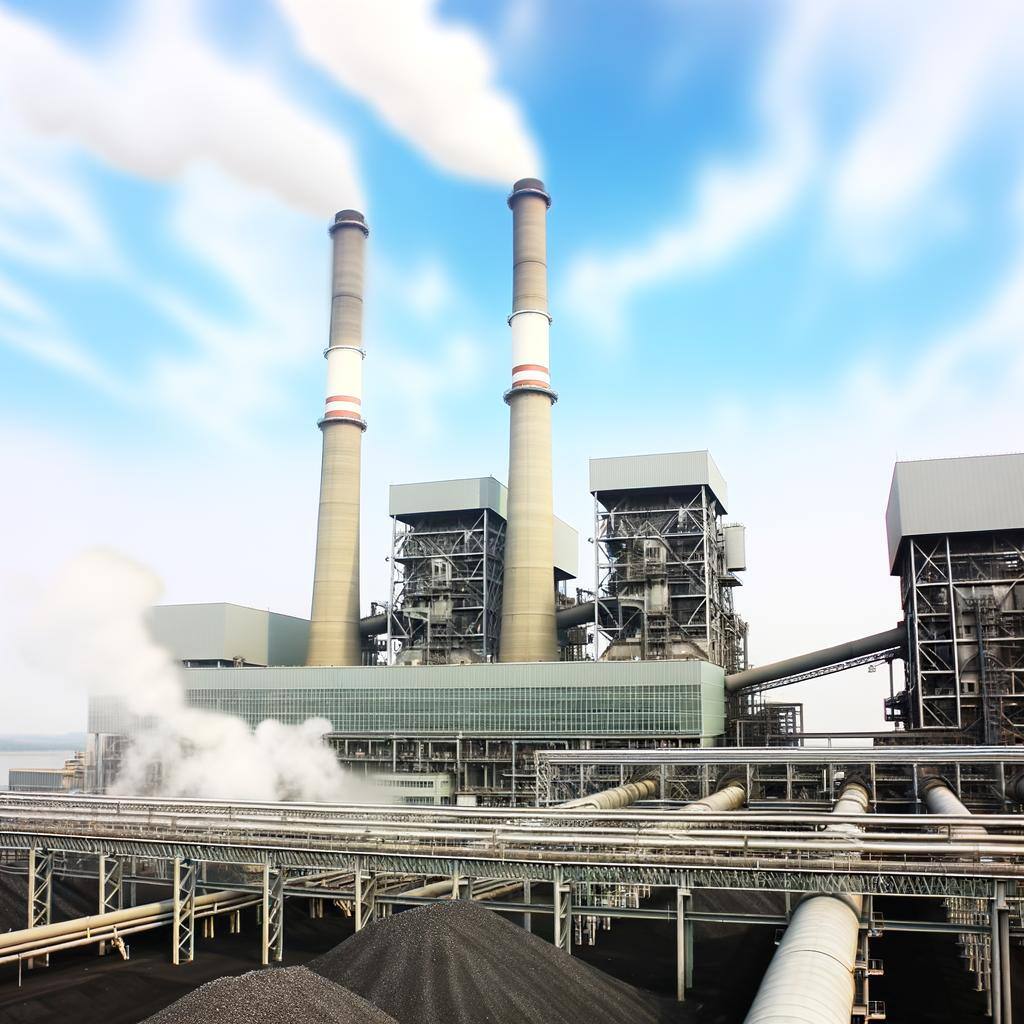
Lignite, or brown coal, is a low-energy, high-moisture coal used in power generation. Despite economic benefits, it has significant environmental drawbacks due to high CO2 emissions.
Coal-fired energy generation produces electricity by burning coal to create steam that drives turbines. It's reliable and economically significant but has major environmental impacts.
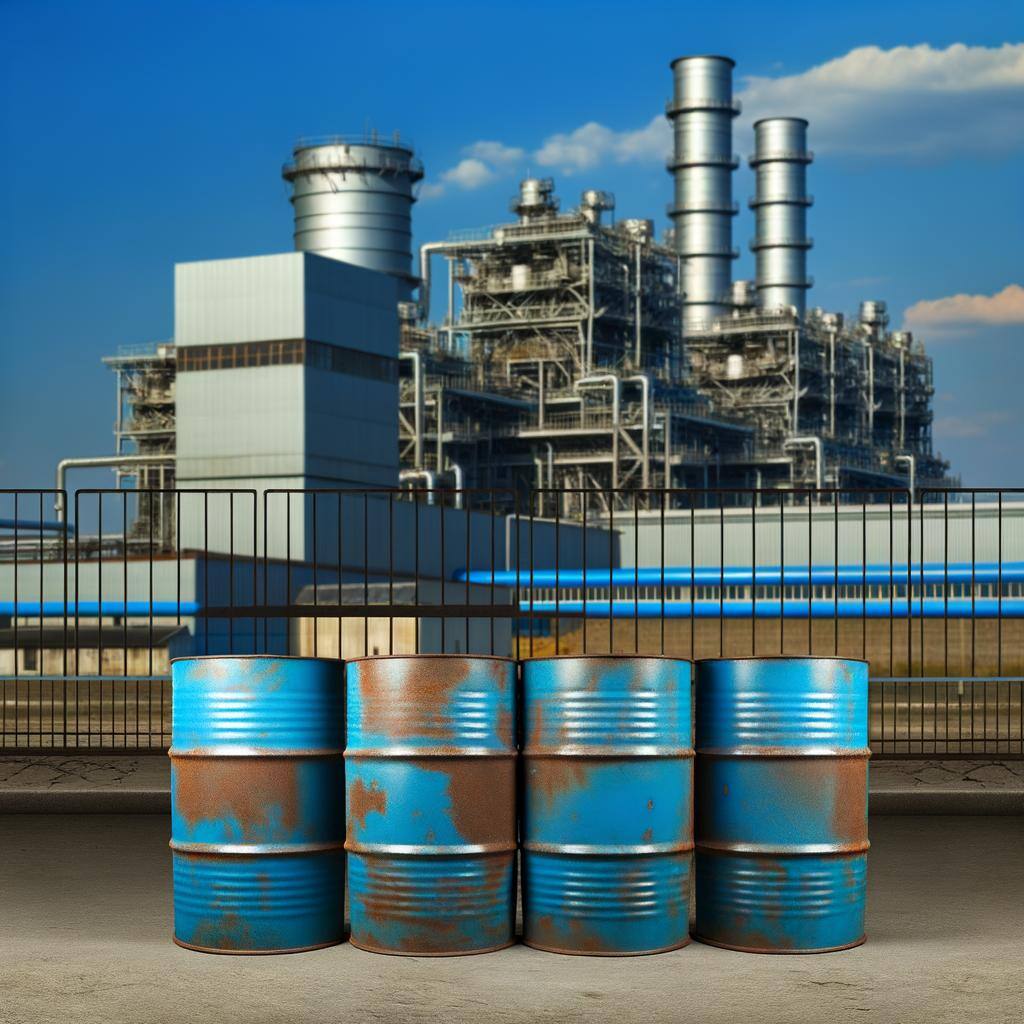
Oil-fired energy generation produces electricity by burning oil. While it offers flexibility and reliability, it faces challenges from environmental concerns and rising renewable energy sources.
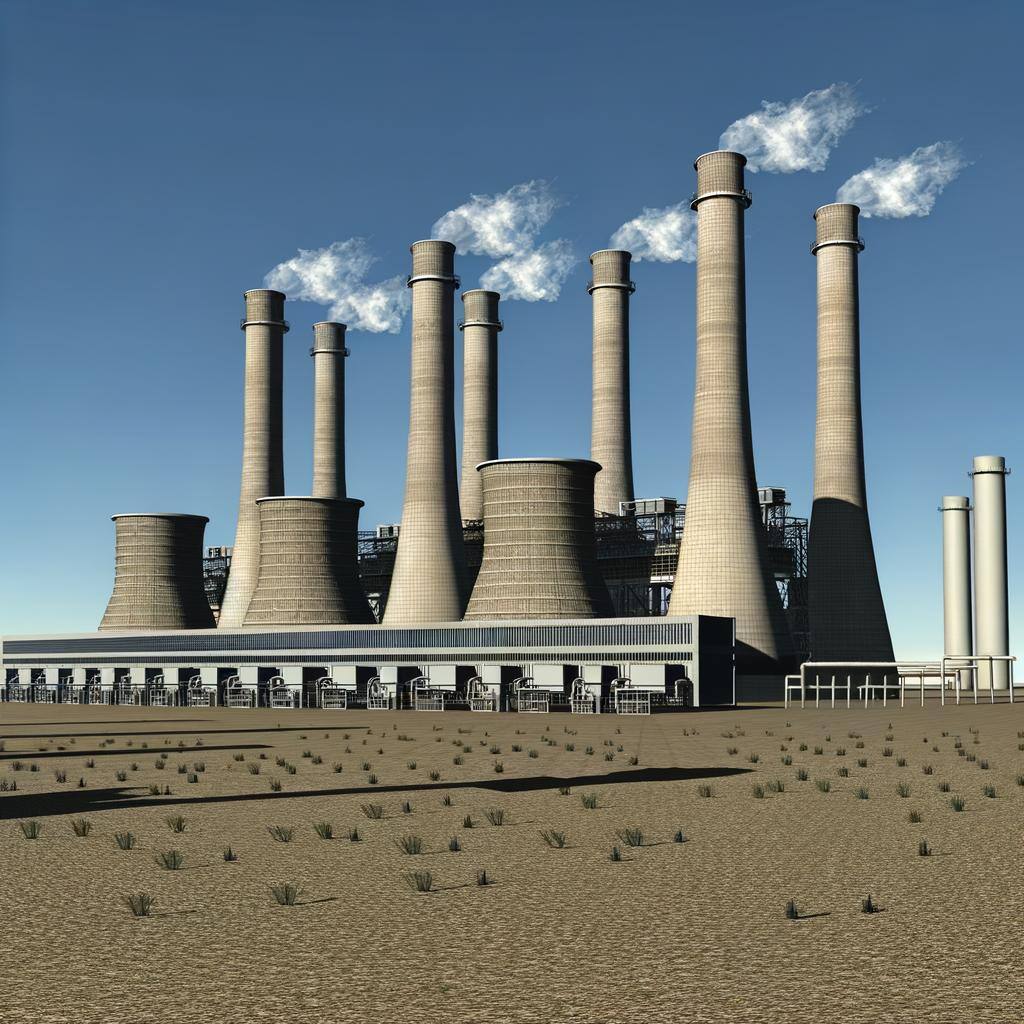
Gas-fired energy generation uses natural gas to produce electricity, offering high efficiency and low emissions compared to other fossil fuels.
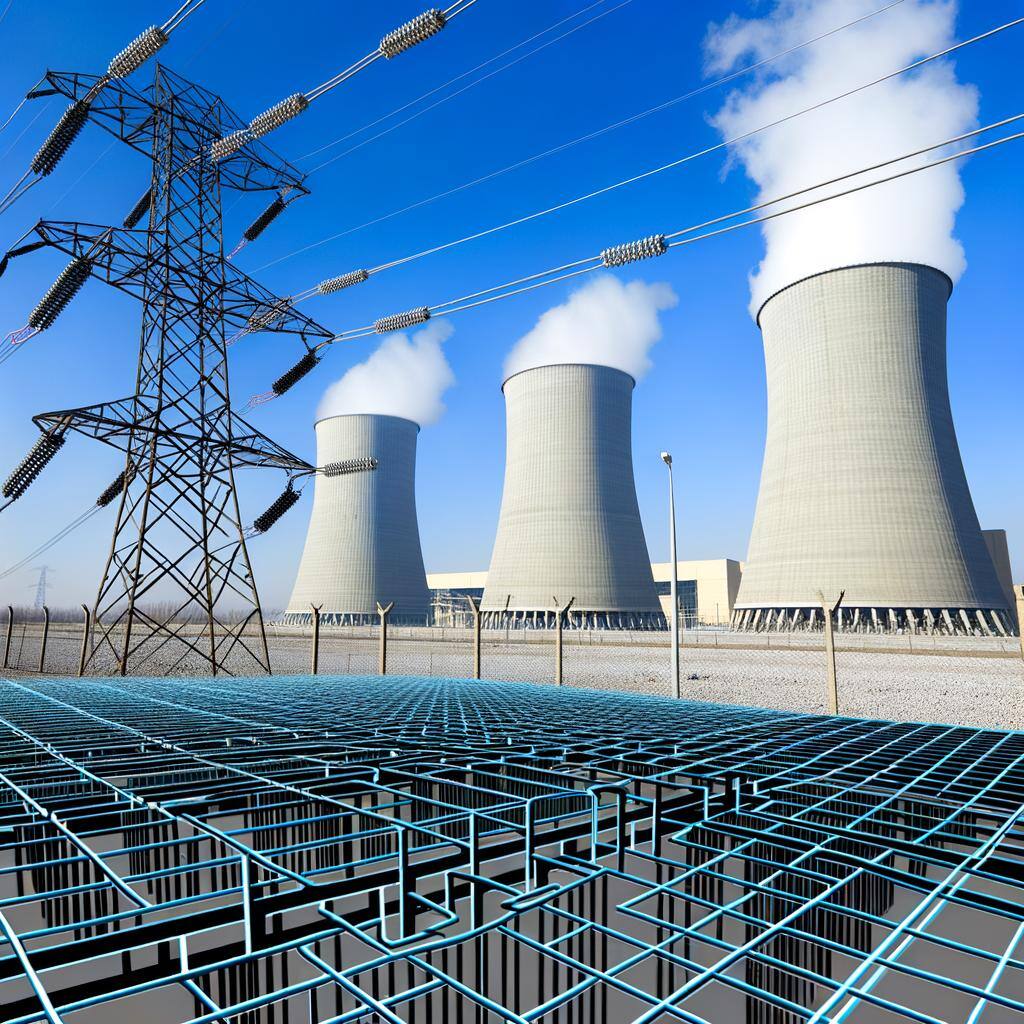
Nuclear energy generates electricity through nuclear fission, where uranium atoms split to release heat. It's efficient and low-carbon, with potential for future fusion energy.
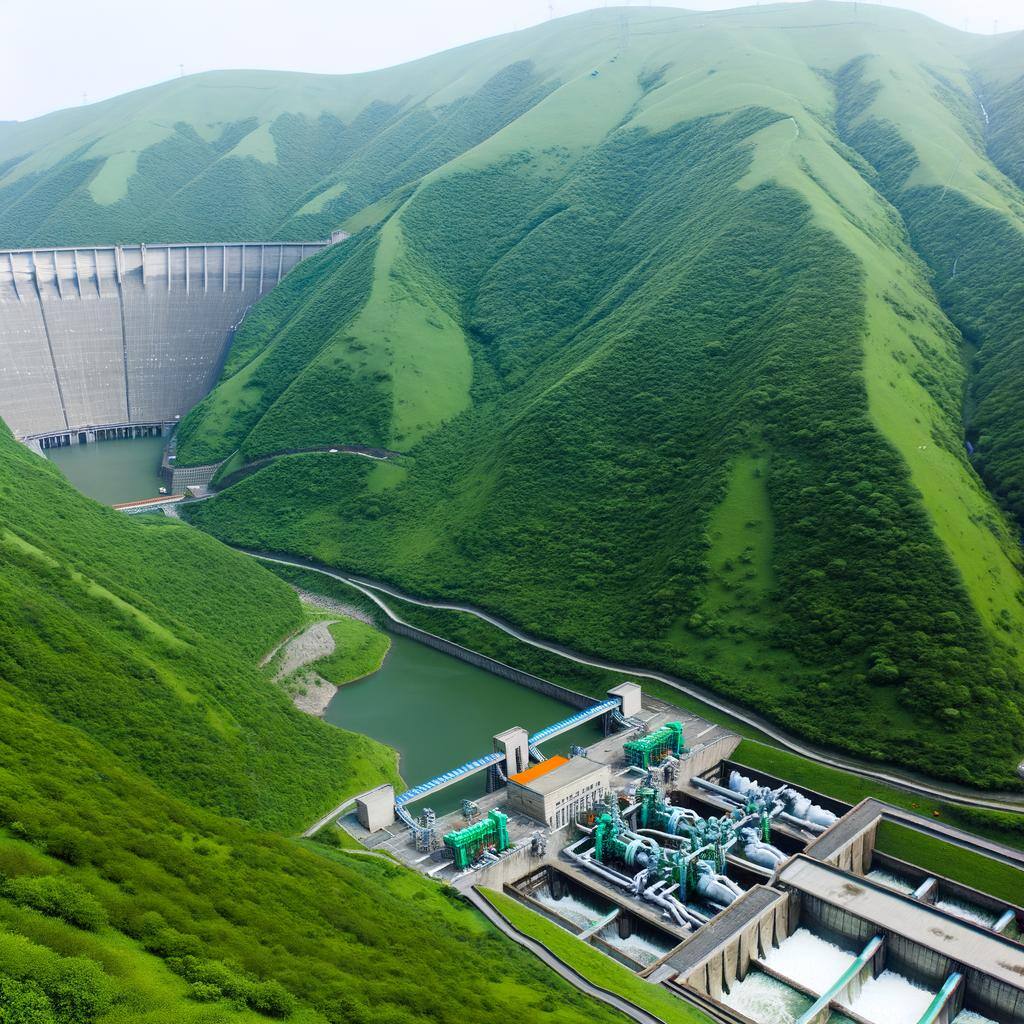
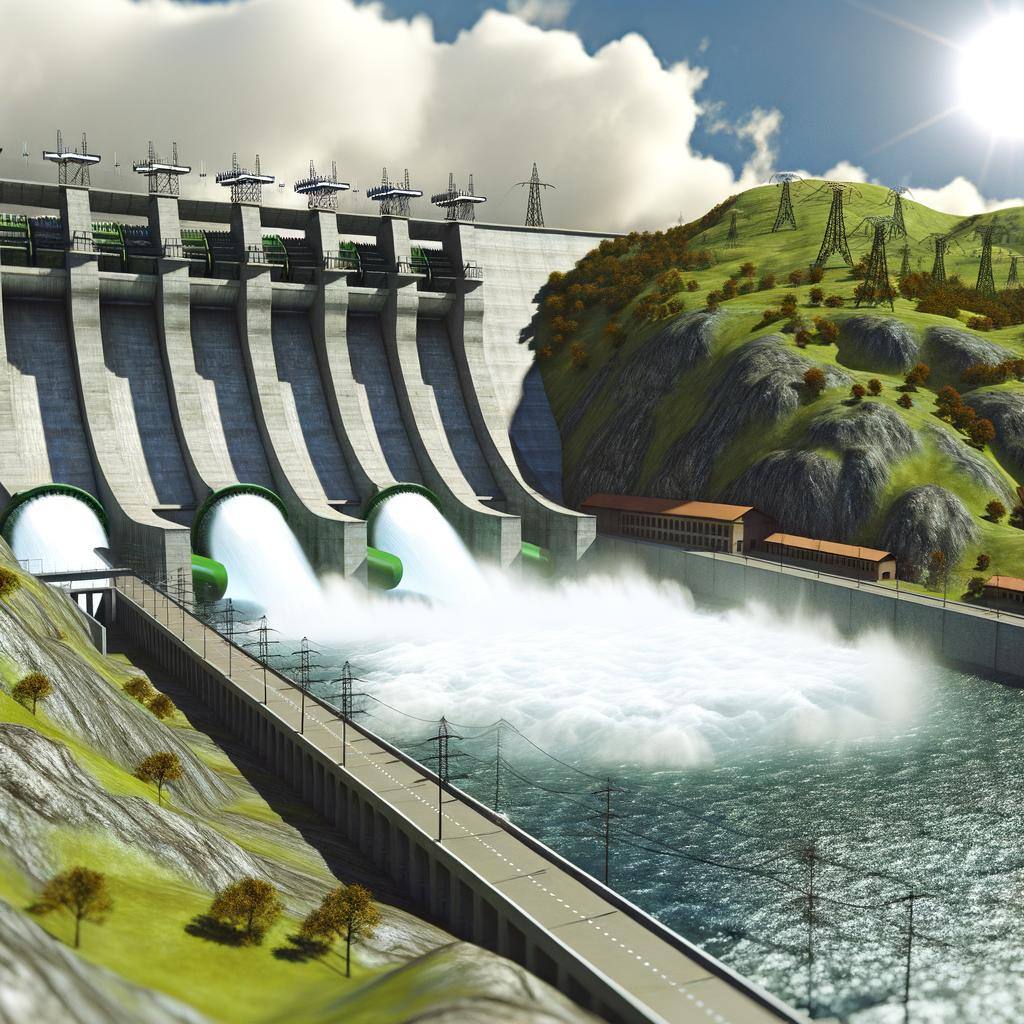
Hydro energy, or hydropower, generates electricity from flowing or falling water. It’s a renewable source with low emissions, using turbines to convert water energy into electrical power.
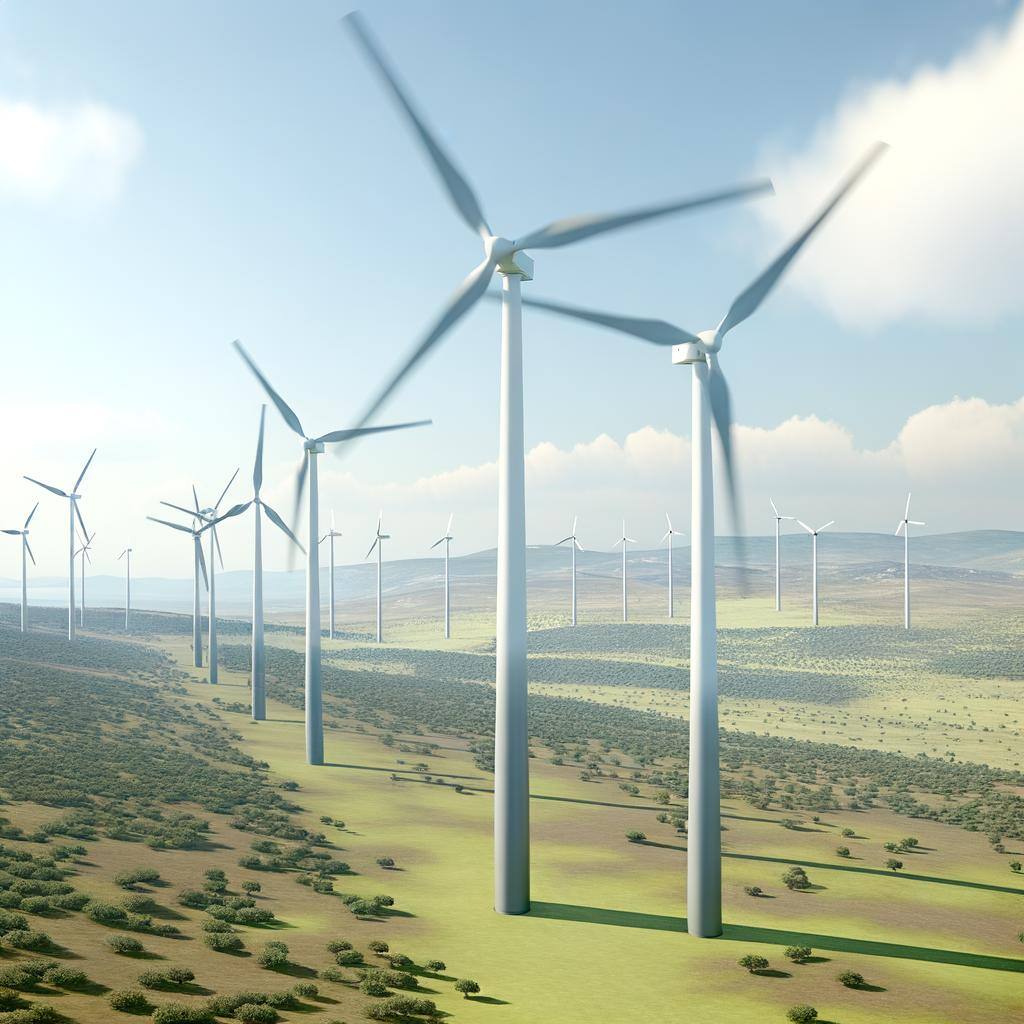
Wind energy is a clean, renewable power source that converts the wind's kinetic energy into electricity using turbines.
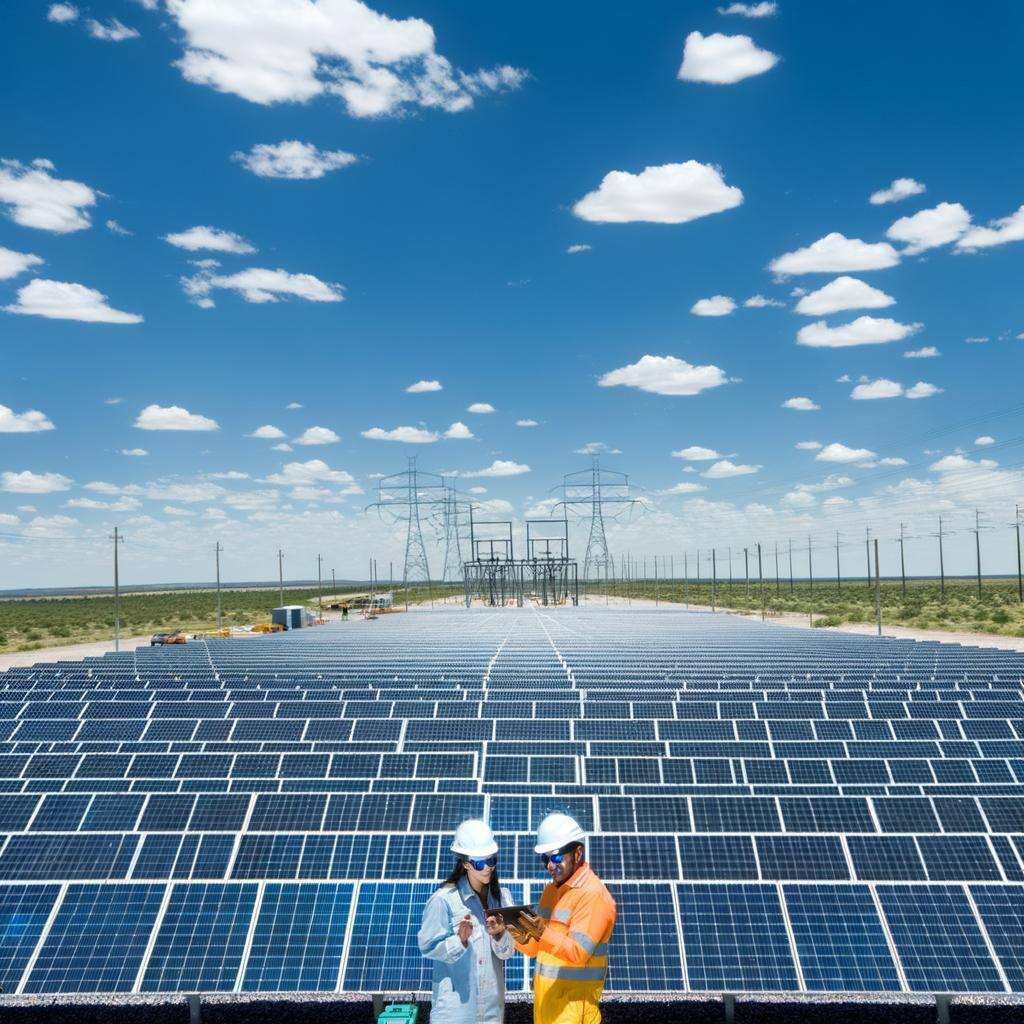
Photovoltaic plants convert sunlight into electricity using solar panels. They offer a clean, renewable energy source, reduce emissions, and are increasingly cost-effective.
Geothermal plants generate power by harnessing heat from the Earth's interior. They use steam or hot water from the ground to drive turbines, producing electricity with minimal emissions.
.png?width=200&height=80&name=etpa-logo-color%20(1).png)


























.png)
.png)