GOPACS by Stefano Zambotti
GOPACS
In the ever-evolving landscape of power markets, Etpa emerges as a pioneer, introducing GOPACS—an innovative platform that is reshaping the dynamics of capacity trading. Developed by Etpa and collectively owned by the Dutch Transmission System Operator (TSO) and all Dutch Distribution System Operators (DSOs), GOPACS is revolutionizing the way participants optimize their assets and contribute to building a greener grid.

Introduction
GOPACS stands at the forefront of energy market innovation, redefining the traditional notions of capacity trading. This groundbreaking platform facilitates seamless capacity trading in the Congestion Market, earning recognition in research papers for its transformative impact and positioning itself as a catalyst for change in the energy sector.
Understanding Grid Congestion
Power grid congestion, a challenge arising from imbalances in electricity demand and supply within specific regions, hinders the efficient delivery of power. Influenced by factors such as geographical limitations, renewable energy integration, and electrification trends (e.g., EVs, heat pumps), congestion poses a critical challenge to grid operators seeking to maintain stability.
CURRENT CONSTRAINTS IN THE DUTCH GRID
Supply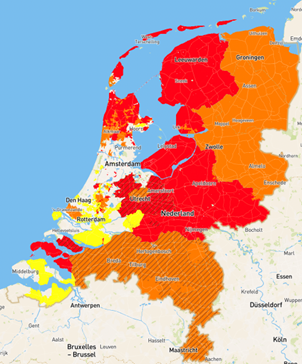 |
Demand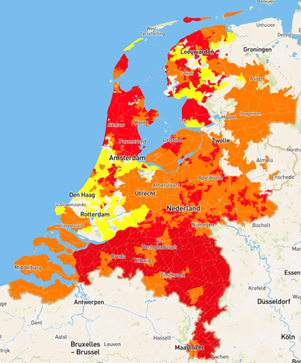 |
Essential Information for Grid Operators
Grid operators need to have access to the following information to be able to solve congestion problems:
This information is reflected in the buying and selling orders quoted in Etpa’s GOPACS order book.
Flexibility for Congestion Services
Assets with flexibility—such as heat pumps, E-boilers, cold storage, batteries, and power plants—qualify for providing congestion services. GOPACS acts as an enabler, allowing these assets to deviate from their nominated positions, contributing to the dynamic management of congestion challenges.
Addressing Congestion Challenges
When system operators foresee a congestion problem in a specific section of the power grid, they publish congestion announcements.
The system operator indicates the period for which it needs capacity, the capacity needed, the congested area, and the time frame for entering orders.
You can find an example of a congestion announcement below:
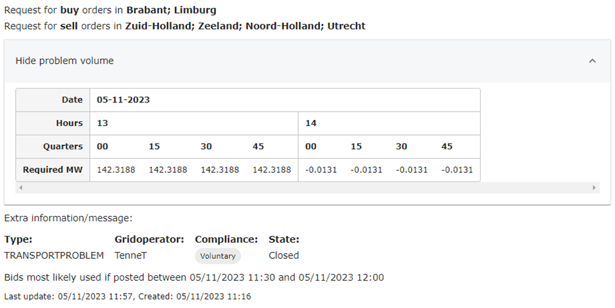
Once the order entry window concludes, the grid operator retrieves all submitted orders, both buy and sell, aimed at preventing congestion and ensuring grid stability. GOPACS then processes these orders, determines the optimal solutions, and communicates back the specific orders that should be activated to achieve these objectives.
ACM’s Code Decision
The ACM's Code Decision, implemented on May 25, 2022, aligns seamlessly with the evolving landscape of the energy transition, where challenges related to grid congestion are on the rise. In this dynamic context, the active engagement encouraged by the Code Decision becomes paramount. Entities capable of contributing their capacity, as highlighted by the decision, not only address congestion issues but also unlock additional revenue opportunities. By providing innovative solutions and embracing the principles outlined in the ACM's decision, GOPACS facilitates a smoother integration of renewable projects, ensuring flexibility, and enhancing overall grid stability.
Some data insights
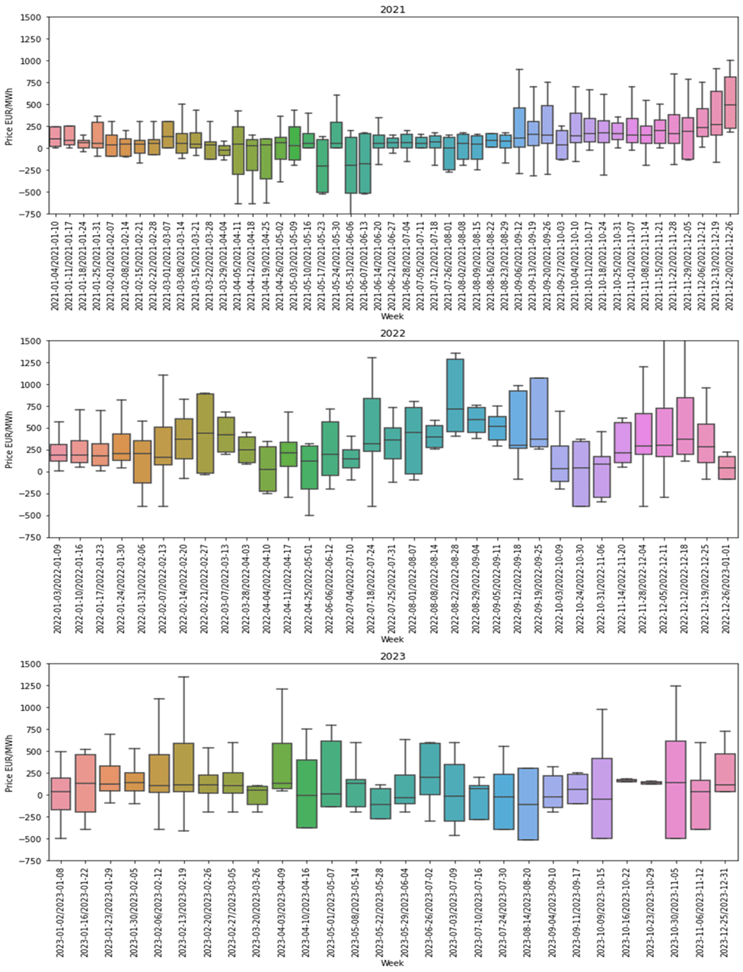
Box: The box represents the interquartile range, which is the range between the first quartile (Q1) and the third quartile (Q3) of the dataset. The length of the box illustrates the spread of the middle 50% of the data.
Whiskers: The whiskers extend from the edges of the box to indicate the range of the data. Any data points beyond the whiskers are considered outliers (if there is any extreme value).
Median Line: A line inside the box represents the median, which is the middle value when the data is sorted. It divides the dataset into two halves, with 50% of the data points below and 50% above.
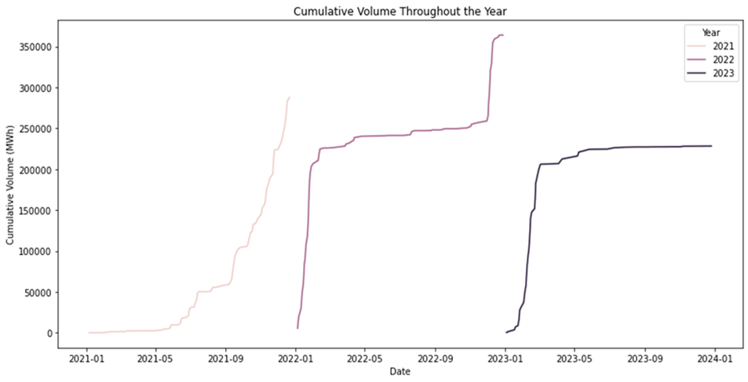
The traded volume witnessed changes across consecutive years: 288,571.2 MWh in 2021, a significant increase to 363,916.8 MWh in 2022, followed by 228,460.8 MWh in 2023.
CONCLUSIONS
GOPACS represents a pivotal advancement in the energy market landscape, offering innovative solutions to address the challenges of power grid congestion. GOPACS not only addresses congestion challenges but also unlocks revenue opportunities for market participants. Aligned with the principles of the ACM's Code Decision, GOPACS embodies the essence of active engagement and contributes significantly to the integration of renewable projects, thereby enhancing grid stability and driving the energy transition forward.